Engine overheating can be due to faults in the water pump, radiator, thermostat or hoses, insufficient coolant, or incorrect venting of the coolant system after work on the cylinder head. Other causes for possible overheating are irregular combustion in the engine due to coke deposits, and high exhaust gas pressure in the case of catalytic converter failure.
TIP
When removing the head gasket, it is important to observe the manufacturer’s instructions, in order to prevent distortions of cylinder head and/or engine block. Make sure that the component sealing surfaces are not damaged during removal of the cylinder-head gasket.

Destruction in the web area due to combustion gas blowby. |
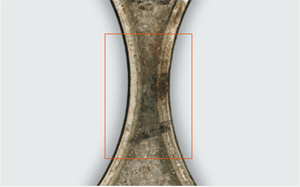
Gas leakage with local blackening of the fire ring bead. Gas leakage with blackening can be the result of insufficient sealing surface pressure or an overheated engine.
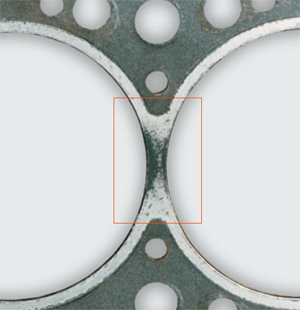
Gas leakage with severe marking due to blowby of hot combustion gases.
|
Oil and Coolant Leakage
As opposed to gas leakage, gasket damage due to oil or coolant leakage is very difficult to detect on a composite head gasket after disassembly. Traces of rust and antifreeze agent with white, lime-like deposits on the gasket surface can be indicators for coolant leakages. Concrete evidence for oil leakage is found very rarely.
Dirt, Foreign Objects, and Rough Surfaces
Practice shows that reference to the importance of clean surfaces is necessary. Repeatedly, pressed-in dirt or foreign objects are the cause for damage and leakage. Therefore, the surfaces of engine block and cylinder head should be cleaned thoroughly. This applies in particular after reworking the surfaces in case of component unevenness, distortion, waviness (deviations in parallelism), or roughness (scores and grooves).
TIP FROM THE EXPERTS
When installing a composite cylinder-head gasket with Viton element, make sure that the cylinder head and the head gasket are positioned accurately. Inaccurate positioning can cause the Viton element to be overpressed or it can become damaged by sharp component edges. Additional sealing compounds should only be applied if this is specified explicitly by the manufacturer

Gasket damage due to dirt and foreign objects.
TIP FROM THE EXPERTS
|

Swelling of composite cylinder-head gaskets due to overheating with steam generation.

Indentation and crushing due to pre-ignition – with and without blowby.The swelling results from the destruction of the gasket material’s silicone impregnating agent, which is not resistant to steam.

Roughness of engine block and cylinder head surfaces leads to gas blowby between the combustion chambers.

Tearing and breakage of the composite material, and damaged Viton element due to incorrect application of additional sealing compound.
|